VoIP data formats
VoIP technology ensures audio, video and data communication via IP based networks including LAN and the Internet. This article focuses on the supported data formats (MP3, WAV, AVI) by Ozeki Phone System. Since it is often required to convert analog signals into digital ones during communication, there is also a short section for explaining supported codecs.
Ozeki Phone System supports various codecs that leads to high quality communication and maximum reliability. (Figure 1)
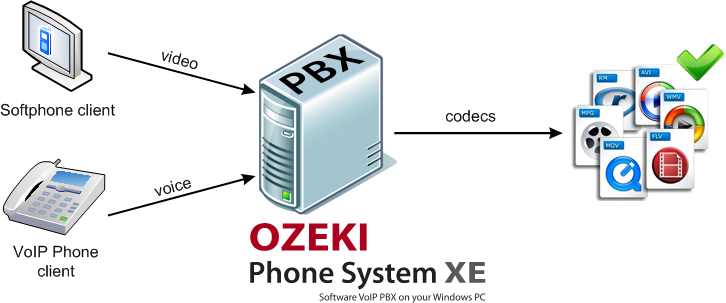
Introduction
For transferring audio and video data over the Internet RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) is used worldwide. Besides other protocols, RTP ensures real-time data transfer between two or more participants. However, for achieving really efficient VoIP communication there is a need for supporting more multi-media formats.
Data formats for VoIP communication
- Audio
- Video
- Data
Efficient transfer of audio data has a critical role in corporate communication. For this purpose, it is ideal to adopt VoIP technology because it offers several audio devices for effective communication. VoIP communication basically only requires a microphone and speakers or headset for oral conversations (Figure 2).
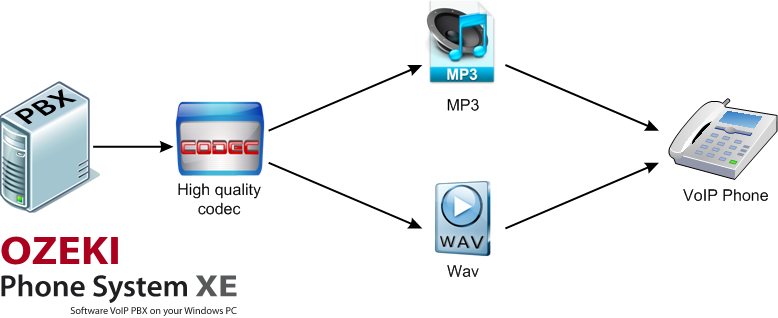
Audio transfer requires to use audio codecs. Audio codecs are computer programs that compress and de-compress digital audio data according to a given audio file format or streaming media audio format using an algorithm. Ozeki Phone System offers built-in audio codecs to provide instant and seamless communication.
These built-in codecs ensures excellent voice quality due to the fact that they integrate advanced digital audio processing functionalities (e.g. echo cancellation, noise cancellation or jitter buffer.
MP3 is a digital audio format that uses a form of lossy data compression. During MP3 compression, the amount of data is significantly reduced while the compressed audio data remains a real reproduction of the original voice. The efficiency of lossy data compression greatly depends on bit rates (bit depth and bit sampling rate).
As opposed to MP3, WAV (Waveform Audio File Format) usually does not compress data itself, however, it is ideal for storing already compressed data. Uncompressed WAV files are large, this way file sharing of WAV files over the Internet is not common. Instead of WAV, MP3 is used for sharing files over the Internet. For storing and playing audio and video data usually AVI format is used.
In order to implement video communication you will need a device for capturing video (video camera or web camera) and a video player. There are various ways for sharing recorded videos (e.g. you can send recorded video data via email). Video chat is also ideal for sharing instant video messages. Video chat is the communication method that allows participants to see and hear each other (using microphone and speakers) during their real time communication. For this purpose, you need a web camera and a software (Ozeki Phone System Webphone) that make participants possible to communicate directly (Figure 3).
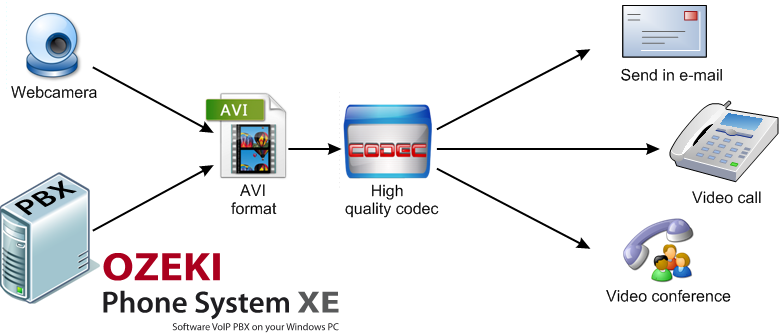
Video codecs are devices or software programs that are able to convert video data into digital format. Ozeki Phone System ensures widespread video codecs for achieving remarkable video chat and video communication experience.
AVI (Audio Video Interleaved) is a multimedia container format that can be used for storing audio and video data. AVI is one of the oldest video formats (has been published in 1992). Its greatest advantage derives from its simplicity that makes it possible to run AVI files on most systems (Windows, Linux, Unix, and most of browsers also support it).
Beside audio and video transfer, VoIP technology also ensures data communication for office users. It means that there are options for sharing various programs and files during communication (Figure 4).
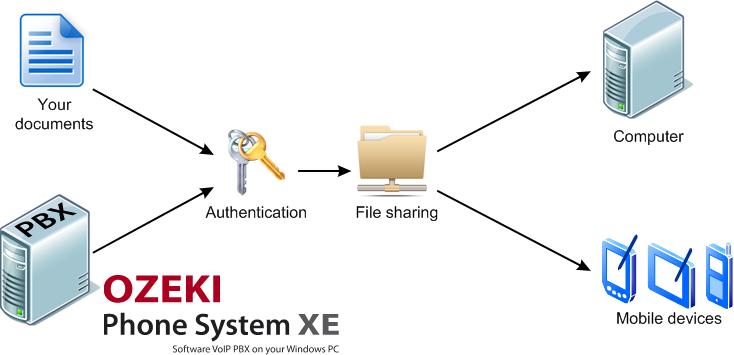
As a result of data communication, employees can really easily share documents and files that highly accelerates daily workflow. This feature can also be boosted during conference calls, as well, because it ensures verification and speeds up business processes. Participants of the conference can easily share contracts, reports and other documents to increase efficiency and save time.
Codecs
Codecs are devices or software programs that are used for converting digital data stream or signal. Encoding is usually made for transmission, storage or encryption of data. Codecs are able to encode a data stream or signal and to decode it for playback or editing. In VoIP technology, codecs are primarily used for converting analog signals into digital signals. There are various types of codecs and they are differentiated by bandwidth, voice quality and other parameters.
Lossy codecs: Lossy refers to the fact that there is some loss of data during compression.
Lossless codec: It refers to the fact that lossless codecs allow to reconstruct the exact original data from the compressed data. Lossless compression is used in cases where original quality is more important than reducing file size. It is especially important if you wish to re-compress the same data later.
Supported codecs by Ozeki Phone System
Ozeki Phone System provides remarkable support for various codecs in order to ensure high-quality audio and video services. It supports more types of audio and video codecs to achieve the best results for converting both video and audio data efficiently.
- G711
- G722
- G729
- iLBC
- Speex
- GSM
In communication it is essential to use the best solutions to provide quality and excellence. For this purpose codecs, such as G711, are used. G711 is an audio codec that has been published by ITU-T, ans also known as Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). It is a frequently used waveform codec. G711 uses a sampling rate of 8000 samples/sec, with a tolerance of 50 parts per million (ppm). G711 codec comes in two different compression algorithms: µ-law and A-law. A-law is the standard compression for international circuits.
A-law: G711 A-law encodes a 13 bit signed linear PCM sample into logarithmic 8-bit sample.
μ-law: G711 μ-law encodes a 14 bit signed linear PCM sample into logarithmic 8-bit sample.
G.722.1 is an ITU-T standard wideband audio codec that allows to convert voice, music and other audio data. It ensures high quality audio, video and conference calls and seamless data transfer for various applications like VoIP, video conferencing, teleconferencing, and Internet streaming applications. Its official name is Low-complexity coding at 24 and 32 kbps for hands-free operation in systems with low frame loss. It uses MLT (Modulated Lapped Transform) and operates on 20 ms audio frames (320 samples). Since G.722.1 is a digital wideband coder algorithm it has an audio bandwidth of 50 kHz to 7kHz and 16, 24, 32 kbps bit rates.
G.729 is an ITU-T standard compression algorithm for audio data that compresses digital voice in packets of 10 ms duration. Its official name is Coding of speech at 8 kbps using conjugate-structure algebraic-code-excited linear prediction (CS-ACELP). G.729 offers high quality, robust speech performance at the price of complexity at a low bit rate (8 kbps). It requires 10 ms input frames and generates frames of 80 bits in length. With G.729 codec processing signals in 10 ms frames and 5 ms look-ahead, the total algorithmic delay is 15 ms.
iLBC(Internet Low Bitrate Codec) is an open source narrowband speech codec. It ensures robust communication over IP networks. Its sampling frequency is 8 kHz/16 bit.
Speex is an open source patent-free voice codec that has been developed for high definition voice over IP (HD VoIP). It provides high quality speech and robust audio transmission using CELP (Code-excited linear prediction) encoding technique. Speex has been designed to compress voice at bitrates ranging from 2 to 44 kbps. Due to its flexibility Speex proves to be a powerful codec. It is well-adapted to Internet applications and provides useful extra features (It offers 3 different sampling rates: narrowband (8 kHz), wideband (16 kHz), and ultra-wideband (32 kHz) compression in the same bitstream, acoustic echo canceller, etc.)
"Global System for Mobile communications" (GSM) is a digital mobile radio system that is widely used worldwide. GSM provides 5,6-13 kbps bit rate and 20 ms frame size. It has two types: Half Rate and Full Rate codecs. They were named after the data channel types that were used. Both Half Rate and Full Rate codecs use a system that is based on LPC (Linear Predictive Coding).
Half Rate: The codec operates at 5.6 kbps (meaning that it uses only the half bandwidth of the Full Rate codec).
Full Rate: It operates at 13 kbps. It was the first digital speech coding standard for GSM. Since it does not ensure high quality speech, it is gradually replaced by EFR and AMR codecs because they offer higher speech quality at lower bit rate.
Keep in mind
Ozeki Phone System offers remarkable support for various VoIP data formats and codecs in order to ensure the best experience during communication. The PBX can excellently handle MP3 and WAV files, as well as AVI formats to store audio and video data. It also supports data communication so you can easily share files, documents during communication (e.g. conference call all participants can receive updated files immediately). In order to convert analog signals into digital signals, Ozeki Phone System also offers extended and outstanding codec support: G711, G722, G729, iLBC, Speex and GSM.
You can find more information on VoIP technology and its instant benefits, as well.
Learn Ozeki Phone System services:
- VoIP network elements
- VoIP protocols
- How to setup a webphone
- How to integrate mobile extensions into the PBX
- How to boost SMS technology in the PBX
More information
- Deatiled description of VoIP network elements
- Understanding VoIP protocols (SIP, RTP, H323)
- Supported VoIP data formats (audio, video, app control, codecs)

 Sign in
Sign in