What is PRI/E1?
This article will give you information about PRI/E1, in other words Primary Rate Interface via E1 line. If you read on you will learn in detail what PRI is, why it is better than analog lines and how it works.
The server of the Ozeki Phone System can receive connections from both a VoIP phone and from the ISDN Network. The only problem is that the ISDN has different needs than IP phones or the internet connection provided by our server (or any other server). So, to fulfill the needs of both types of networks, PRI/E1 cables are installed, which provide the necessary connection to us, as seen in Figure 1.
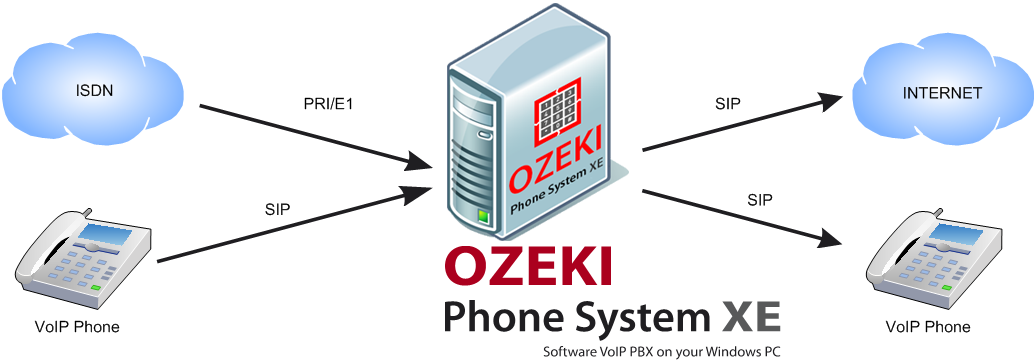
PRI is a level of service of the ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network, a set of international standards about all-digital public telecommunications networks) network, connecting two end lines. Several B-channels or bearer channels, carrying the data, voice and other services, and D-channels or data channels, controlling and signaling information, are included into it.
Why is PRI/E1 better than separate analog lines?
- Calls can be established faster with PRI/E1.
- Your conversations will stay more private, since digital lines are harder to be tapped into.
- Digital lines are a lot more reliable and the voice transmitted via them is a lot clearer.
- Voice and data can be transferred at the same time with PRI/E1, and you can also use video conferencing, faxing, simultaneously as well, by using different channels.
- Uneven distribution of calls would be avoided.
- There would be no need to wait for an Auto-Attendant, as calls would be transferred directly to the appropriate extension.
- Each extension would have a unique ID (identity, a number for identification).
Larger organisations would require a lot of trunk lines, so analog trunks might not be their best idea since they would need to separate the analog trunk cards to end these lines in their PBX (Public Branch eXchange, which handles with the inside and outside calls of a local network) with a separate rental fee for each line, where the capacity of individual lines to provide free calls might not even be fully used.
As a result, these organisations should get a digital line called a PRI/ E1 in most countries of the world. You can promote 30 different conversations simultaneously. It is made possible by multiplexing/ de-multiplexing techniques at both ends.
How it works
64 Kbps is the capacity of data transmission on each channel. PRI/E1 can connect to both analog trunk lines and also IP PBX systems, although you might need a PRI Card to terminate the PRI circuit on the PBX. Two PBX systems can also be connected by it, so it can provide up to 30 channels between them.
PRI/E1 has 30 B-channels (Bearer channels) and one D-Channel (data-channel). So, with it, you can have up to 2048 Mbps service in most countries. It connects a pbx to the central office of the local or a long distance telephone company.
PRI/E1 connects the server of the Ozeki Phone System to the ISDN network, so there is no need to be worried about your Internet connection, since the Ozeki Phone System can provide you with the best service available regardless of the type of Internet connection that you have.
These articles have more information about certain topics. Read them to know more:
- What is PRI?
- What is PRI/T1?
- What is PRI/J1?
- What is ISDN NT?
- What is ISDN TE?
- What is PABX?
- What is IP PBX?
- What is VoIP PBX?
More information
- What is VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)?
- What is SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)?
- What is PABX (Private Automated Branch Exchange)?
- What is IP PBX? (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange)
- What is VoIP PBX (Voice Over Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange)?
- What is SIP Trunking (Session Initiation Protocol Trunking)?
- What is SIP Trunk (Session Initiation Protocol Trunk)?
- What is Direct Dial In: DID?
- What is IVR (Interactive Voice Response)?
- What is RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol)?
- What is RTCP (Real-time Transport Control Protocol)?
- What is SRTP?
- What is H323?
- What is VoIP Tunnel?
- What is PSTN Gateway?
- What is CAPI?
- What is FXO?
- What is FXS?
- What is PRI/E1?
- What is PRI/T1?
- What is PRI/J1?
- What is PRI?
- What is ISDN NT?
- What is ISDN TE?
- What is VoIP Client (Voice Over Internet Protocol Client)?
- What is SIP Client?
- What is SIP Server?
- What is VoIP Server (Voice Over Internet Protocol Server)?
- What is Dial Plan?
- What is Asterisk?
- What is VLAN?
- What is VoIP Phone?
- What is SIP Phone?
- What is IP Phone?
- What is SIP Account?
- What is ATA?
- What is Ring Group?
- What is Virtual PBX?
- What is Hosted PBX?
- What is PSTN?
- What is SDP (Session Description Protocol)?
- What is DECT?
- What is VoIP Call?
- What Is VoIP Cluster?
- What is Trunk?
- What is Fring?

 Sign in
Sign in