What is PRI/J1?
This page is about PRI/J1 or Primary Rate Interface via J1 line. Get informed about the operation of this line and what kind of benefits it has over analog lines.
PRI/J1 provides a connection between the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN, which is a set of international standards that specify the access to advanced digital networks) and the server of Ozeki Phone System. Through this, data, voice and video can be transmitted. Once they have arrived to our server, they get sent to the proper destination, to either one of the VoIP phones or computers connected to the Internet as shown in Figure 1.
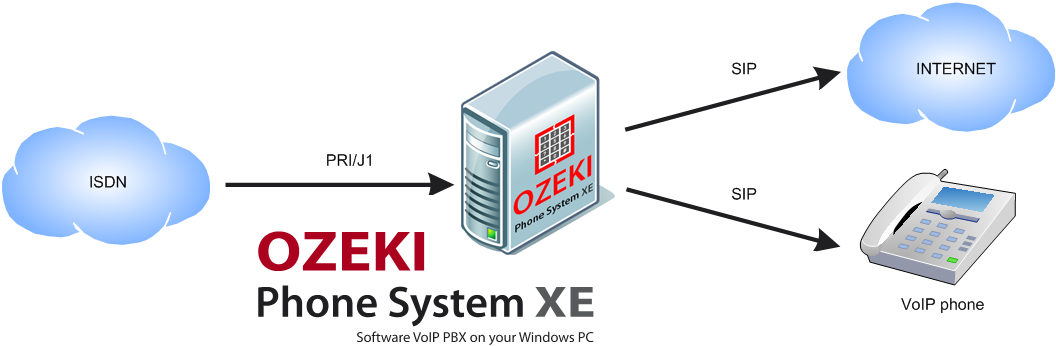
What PRI/J1 is about and how it works
Getting a PRI/J1 line would solve many problems of larger organizations, to replace several analog trunks, to avoid using separate analog trunk cards, which would terminate all of those lines in their PBX, while each analog line would require separate rental, and the possibility of free calls via individual lines would not be fully used.
PRI/J1 is a level of standard communication, which is made of copper wires and it consists of 23 B-channels, to carry data, voice and other services and one D-channel, to signal and control information. J1 is a slightly modified Japanese version of the North-American T1, with which you can have as high as 1544 Mbps service. PRI/J1 is able to connect a PBX to a central office of a telephone company or a long distance phone company.
On each channel, data transmission is 64 Kbps fast. It can be connected to analog and Internet Protocol Private Branch eXchange (IP PBX the next generation of PBX, which is responsible for handling calls in a local network from the inside and from the outside) systems, or to two PBX systems at the same time (giving them both 24 channels). If an analog and an IP PBX system is connected with it, a PRI Card is necessary to terminate the PRI circuit on the PBX.
A digital line called PRI/J1 is used by large organisations in Japan. These lines have the capacity to carry up to 24 channels of voice communications at the same time with multiplexing/ de-multiplexing techniques.
A PRI/J1 Card is necessary to terminate the PRI/J1 line in the customer's PBX. Then only one line would be enough to supply the capacity of 24 independent conversations simultaneously through it with only a single rental package provided by the local telephone company.
Benefits of a PRI/J1 over separate analog trunk lines:
- Caller ID's are provided to all extensions.
- Call distribution would be even.
- PRI/J1 gives you the possibility of a faster call-establishment.
- High voice quality is carried via digital lines.
- The proper extension is directly connected without an Auto-Attendant.
- Data and voice can be sent through various channels at the same time as a video conference is held or a fax is being sent.
- Conversations would be harder to listen to, giving you more reliability and privacy through PRI/J1 connections.
The server of The Ozeki Phone System is completely able to serve even those ISDN networks that use PRI/J1 as connection to it. Any information that arrives from a PRI/J1 is transmitted through SIP as if it was coming from the local network. The Ozeki Phone System is the only server with such an amount of multifunctionality.
The following pages contain information in other areas in connection with this article. Read them to find out more.
- What is PABX?
- What is IP PBX?
- What is PRI?
- What is PRI/E1?
- What is PRI/T1?
- What is ISDN NT?
- What is ISDN TE?
More information
- What is VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)?
- What is SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)?
- What is PABX (Private Automated Branch Exchange)?
- What is IP PBX? (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange)
- What is VoIP PBX (Voice Over Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange)?
- What is SIP Trunking (Session Initiation Protocol Trunking)?
- What is SIP Trunk (Session Initiation Protocol Trunk)?
- What is Direct Dial In: DID?
- What is IVR (Interactive Voice Response)?
- What is RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol)?
- What is RTCP (Real-time Transport Control Protocol)?
- What is SRTP?
- What is H323?
- What is VoIP Tunnel?
- What is PSTN Gateway?
- What is CAPI?
- What is FXO?
- What is FXS?
- What is PRI/E1?
- What is PRI/T1?
- What is PRI/J1?
- What is PRI?
- What is ISDN NT?
- What is ISDN TE?
- What is VoIP Client (Voice Over Internet Protocol Client)?
- What is SIP Client?
- What is SIP Server?
- What is VoIP Server (Voice Over Internet Protocol Server)?
- What is Dial Plan?
- What is Asterisk?
- What is VLAN?
- What is VoIP Phone?
- What is SIP Phone?
- What is IP Phone?
- What is SIP Account?
- What is ATA?
- What is Ring Group?
- What is Virtual PBX?
- What is Hosted PBX?
- What is PSTN?
- What is SDP (Session Description Protocol)?
- What is DECT?
- What is VoIP Call?
- What Is VoIP Cluster?
- What is Trunk?
- What is Fring?

 Sign in
Sign in