What is ISDN NT?
This page is about the Network Termination device of the Integrated Services Digital Network. It contains information about what kind of integrated services are available with ISDN NT, what kind of components it has (channels and access types) and you get to know the ISDN devices.
The Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of international standards set by a branch of the United Nations' International Telecommunications Union, for access to advanced, all-digital public telecommunications networks.
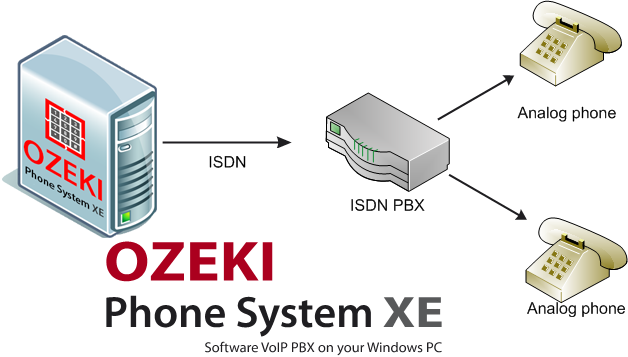
As Figure 1 shows, here our ISDN NT device (explained at the bottom of the page) is a Private Branch eXchange (PBX, which is responsible for connecting the caller to the desired extension regardless of whether one of them is outside the local network), which serves as an exchange between analog telephone lines and the ISDN connection provided by the server of Ozeki Phone System. This is the device that distributes the phone lines based on the ISDN Network.
Integrated Services
Currently, diverse access techniques and standards and a mixture of analog and digital transmission methods are used. Full-motion video, graphics/video/voice conferencing, electronic mail and high-speed facsimile will also be provided by telephone networks. ISDN integrates all these with standard interfaces and access protocols to all services. As it is international, the interfaces and access protocols are the very same all over the world.
Digital
ISDN system is entirely digital, including customer-premises equipment (like telephones or fax machines), the carrier's trunk network, the local access loop, switching and signaling.
Network
ISDN has a common set of standards, which operate worldwide transmissions and switching services, with the control of the various operating companies and national telecommunications authorities.
Components of ISDN
ISDN Channels
- B (Bearer) Channel: it's a 64 Kbps unit of clear digital bandwidth, carrying voice, data or video without restrictions on format or protocol.
- D (Data) Channel: it's a signaling channel, carrying information to connect or disconnect calls and special calling parameters. It's not a clear channel and the data rate of it is 16 Kbps with Basic Rate Access, and 64 Kbps with Primary Rate Access. Its most important function is signaling with end-to-end significance.
- H (High-capacity) Channel: it's a special, high-speed clear channel, designed for full-motion colour video. H-zero operates at 384 Kbps, while H1 does at 1536 Mbps.
ISDN Access Types
- Basic Rate Access: for individual users and small businesses. It has two 64 Kbps B channels (one voice-conversation, one medium-speed data session) and one 16-Kbps D channel (for signaling), and an additional 48 Kbps bandwidth for maintenance.
- Primary Rate Access: it provides high-capacity service to large customers for applications such as pbx-to-pbx trunking. In North-America and Japan 23 B+D works at 1544 Mbps (23 B, 1D or 4 H0 or 1 H11 channels) In the rest of the world 30 B+D operates at 2048 Mbps (30 B, 1D, or 5 H0 or 1 H12 channels)
ISDN Devices
- Terminal Equipment (TE)
- Network Termination 1 and 2 (NT1 and NT2)
The NT devices are boundaries between the customer's premises and the carrier's network. They either perform local signaling (or logical interface functions) or the physical interface conversion between the various customer and network sides of the interface. Most of the time, a PBX or digital multiplexer performs both physical and logical interface functions. It is usually called NT.
As ISDN is connected to the Ozeki Phone System, the sessions coming from or going there are always great. Only Ozeki Phone System is capable of providing impeccable service at all times on all networks and devices due to its incomparable multifuncionality.
Check out the following articles for more information:
More information
- What is VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)?
- What is SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)?
- What is PABX (Private Automated Branch Exchange)?
- What is IP PBX? (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange)
- What is VoIP PBX (Voice Over Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange)?
- What is SIP Trunking (Session Initiation Protocol Trunking)?
- What is SIP Trunk (Session Initiation Protocol Trunk)?
- What is Direct Dial In: DID?
- What is IVR (Interactive Voice Response)?
- What is RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol)?
- What is RTCP (Real-time Transport Control Protocol)?
- What is SRTP?
- What is H323?
- What is VoIP Tunnel?
- What is PSTN Gateway?
- What is CAPI?
- What is FXO?
- What is FXS?
- What is PRI/E1?
- What is PRI/T1?
- What is PRI/J1?
- What is PRI?
- What is ISDN NT?
- What is ISDN TE?
- What is VoIP Client (Voice Over Internet Protocol Client)?
- What is SIP Client?
- What is SIP Server?
- What is VoIP Server (Voice Over Internet Protocol Server)?
- What is Dial Plan?
- What is Asterisk?
- What is VLAN?
- What is VoIP Phone?
- What is SIP Phone?
- What is IP Phone?
- What is SIP Account?
- What is ATA?
- What is Ring Group?
- What is Virtual PBX?
- What is Hosted PBX?
- What is PSTN?
- What is SDP (Session Description Protocol)?
- What is DECT?
- What is VoIP Call?
- What Is VoIP Cluster?
- What is Trunk?
- What is Fring?

 Sign in
Sign in