H.323 vs. SIP
Transmitting data, audio and video signals used to be quite challenging in the previous decades, but it is not anymore. They are defined by various protocols, and once you have learnt what those protocols are and how they work, understanding data transmission will not be a challenge for you either. So if you are wondering if it can really be explained so simply, check out our page and watch the video at the bottom.
A set of rules regulating data transmission among computers is called a protocol. Data needs to be compressed into data packets and then broken into codecs to be sent to another computer in a network of more than two computers. However, it would get lost in the network unless we know where to send them.
It means that we need to address them somehow, so each computer needs to have an address also. These specific addresses are called IP (Internet Protocol) addresses.
H.323 is a VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol, which controls multimedia transmission over the Internet) protocol, set up by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU). It controls data, audio and video transmission through the Internet. Service providers use it in real-time applications, to provide audio and viceo services. VoIP uses it to have its traffic transmitted via its networks.
It defines network elements such as terminals, gateways, gatekeepers and so on. To build up communication, you need at least two terminals (Figure 1).
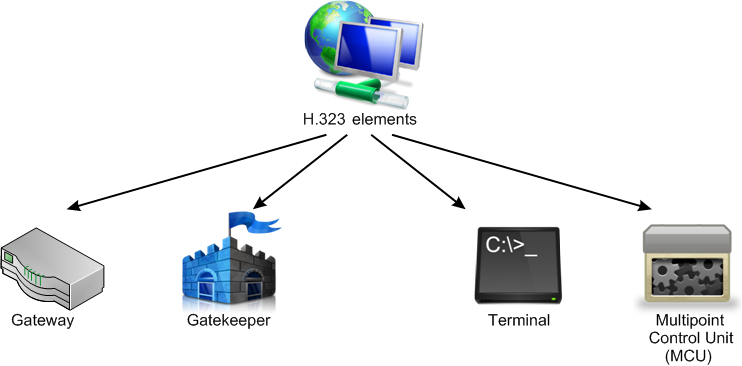
H.323 elements:
- Gateway: they make communication possible between H.323 and ISDN or PSTN
- Gatekeeper: they offer services such as admission control, address solution, end-point registration and so on. They are optional.
- Terminal: They can be video-conferencing systems, IP phones or VoIP phones. They are the most important elements in the communication process.
- Multipoint Control Unit (MCU): It helps us make video calls, mixes and switches video with multipoint conferences with two elements: MC (multipoint controller) and MP (multipoint processor).
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): initiates the session, so it starts a call line and terminates it in the end. It sets up real-time multimedia sessions between the endpoints. Instant messaging and audio and video conferences can be organized, and voice and video calls can be made with it.
In all phoning technologies, a dial has the same phases:
- Connect the participants by setting up the line - SIP does it.
- Phase of data transfer: information packages are being sent - H.323 protocol does it.
- Disconnecting the call - sip does it.
Ozeki Phone System uses sip protocol to set up and terminate a communication session, because Ozeki Phone System always chooses the best and quickest solutions to satisfy your needs. If you choose Ozeki Phone System, you can make sure that the communication of the future will move into your home, and it will provide you easy-to-use interfaces, flexibility and the latest technology, from a company of high expertise.
These articles have more information about certain topics. Read them to know more:
- VOIP explained
- SIP Protocol explained
- What is PSTN?
- ISDN NT vs ISDN TE
- What is VoIP Phone?
- What is IP Phone?
For a better understanding, please watch our video:
H.323 vs. SIP (Video tutorial)
