SIP Protocol Explained
If you think you need innovative solutions in communication, then you should learn a few facts about the base of the most modern communication technologies, the SIP (Session Initiation Protocol. Its definition can be read below.) Protocol. If you read on, you will read about internet protocols in general as well as SIP especially, then you will learn how it works, and what it can give you, some of which you might have never thought of.
Protocols were designed to serve as standard sets of rules to regulate data transmission among computers. Data are sent compressed in data packets if two or more computers take part in the session. Then they only need an address to arrive at the desired computer.
IP address is what is used in such cases. IP (The Internet Protocol) is used to transmit data packets over the Internet. That is why each computer needs a unique IP address, to be able to send and also receive data packets.
SIP is a core protocol, which establishes sessions on the Internet. It transports information on session description from the caller to the callee, allows parameters to be changed in the middle of a session and it ends the session (Figure 1).
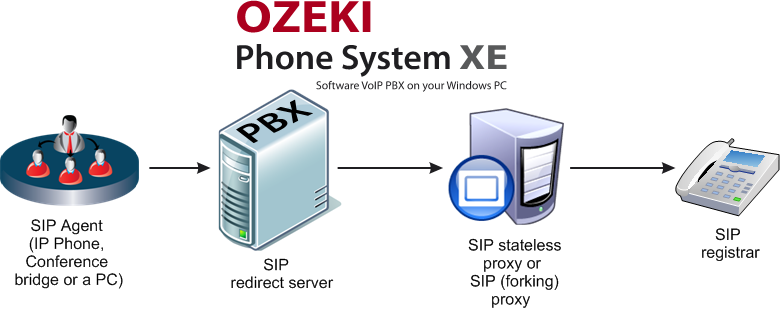
SIP is built of certain blocks
(as shown in Figure 1 above):- SIP user agent can be an IP phone, a conference bridge or a personal computer
- SIP redirect server can return new location for requests
- SIP stateless proxy can route call requests
- SIP (forking) proxy is also intended to route call requests
- SIP registrar can keep mappings between names and addressees
SIP-based services:
- Caller ID: plus extensions
- Call hold: you can set every media address individually to 0.0.0.0
- Call forwarding: if you don't wish to answer certain calls you can forward them to another IP address.
- Call transfer: Having answered the call you can transfer it to someone else's IP address.
- Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency carriage: it carries the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network, or the telephone network that we are used to for decades) numbers via RTP's (Real-time Transport Protocols define a standardized packet format for delivering audio and video over IP networks).
- Voice mail: User agent with a special URL and Real-Time Streaming Protocol if possible (RTSP allows to control multimedia streams delivered).
- Calling Card with a voice server
No matter if we talk about PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network, or the old, analog telephone network) or Internet-based telephoning, the call has three phases:
- SIP protocol sets up the call line and connects the participants.
- Other protocols perform the data transfer, once the call line has been set up.
- SIP terminates the call in the end.
If you wish to build an audio or video based application, SIP protocol is kindly advised for you to use, as SIP is able to set up real-time multimedia sessions, to give the users the opportunity to make video and voice calls and conferences and IM conferences.
SIP Protocol is a key element of Ozeki Phone System, the system that can offer you the highest expertise, multifunctionality and advanced technology. Ozeki Phone System will finally make you believe that the latest developments are not necessarily complicated, since it is very easy to manage, but it still provides the next generation of communication services.
These articles have more information about certain topics. Read them to know more:
