What is FXO?
This page is intends to explain how an old-fashioned telephone system works in order to give you a broader insight into new generation systems. Get to know how the FXO ports work, how you can make and receive calls with the help of this port and why Ozeki Phone System is an excellent choice.
FXOs or Foreign eXchange Offices are those little ports in your phones or fax machines at home or in your office, into which you plug the phone cable in. This is where ring voltage, battery current and dial tone enters your device.
It is always combined with an FXS or Foreign eXchange Subscriber, which is the plug on the wall, providing the analog line. If you have a PBX (Private Branch eXchange)you can install it between the FXO and the FXS, to give you the connection between the analog phone system or the traditional pbxs and the VoIP system or to install it to each other via the Internet.
You can also connect your traditional phone to the internet if you obtain a certain device that can synchronize several technical devices. These are called adapters, or ATA's (Analog Telephone Adapters, which connect Internet-based telephone system to the analog system) in our case. This is the agent, through which direct communication happens between an analog phone and a VoIP server without installation of any further programs.
How do these ports work?
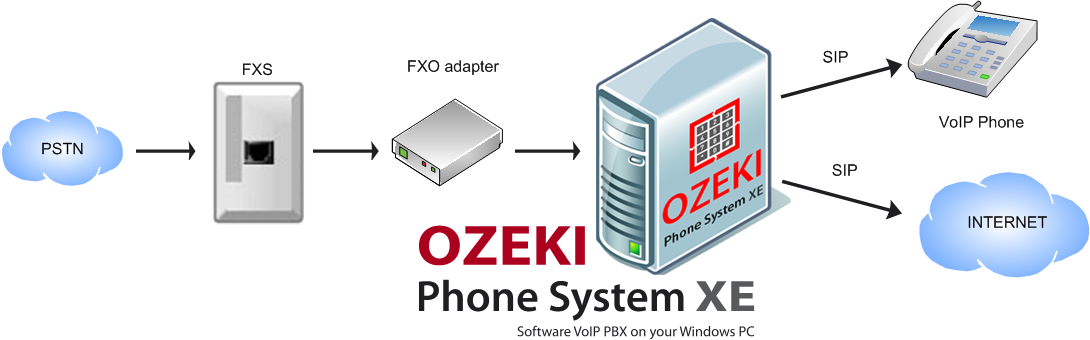
The role of an FXO, and the process in which it is included is shown in Figure 1, and explained below.
- A call is made on a device somewhere in the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network, the original telephone network).
- It arrives at the FXS port.
- It is forwarded to the FXO port via cable.
- It arrives at the server of Ozeki Phone System, connected to the FXO.
- It is transmitted to either the VoIP phone or the Internet
Making a call
- You pick up the phone at the FXO end, the FXS end is notified about this.
- You dial on your FXO device, and the number is forwarded to the FXS port and to the service provider.
Receiving a call
- From your service provider, a call arrives at the FXS port, which sends a slight voltage to the FXO port.
- Your phone is ringing.
- You answer the call on your device connected to the fxo port, which is transferred to your FXS port, then to your service provider, then to the fxs port of the person you are talking with, then to the device connected to his or her FXO port.
The speed and quality of data transmission through your FXO depends on where you get them from. Ozeki Phone System will always provide the quickest and best data transmission available to your FXO port.
Check out the following articles for more information:
For a better understanding, please watch our video:
What is FXO? (Video tutorial)
