What is PRI?
At this site you will be informed about Primary Rate Interface, or PRI. If you are interested in getting telecommunications services to your office, and how it would work with the help of a high capacity digital circuit, you should read on.
PRI is an end to end digital circuit, and as such, it is a level of service of the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN, which internationally sets down the rules of access to digital, advanced networks). It consists of several B-channels or bearer channels, which carry the data, voice and other services, and D-channels or data channels, which control and signal information.
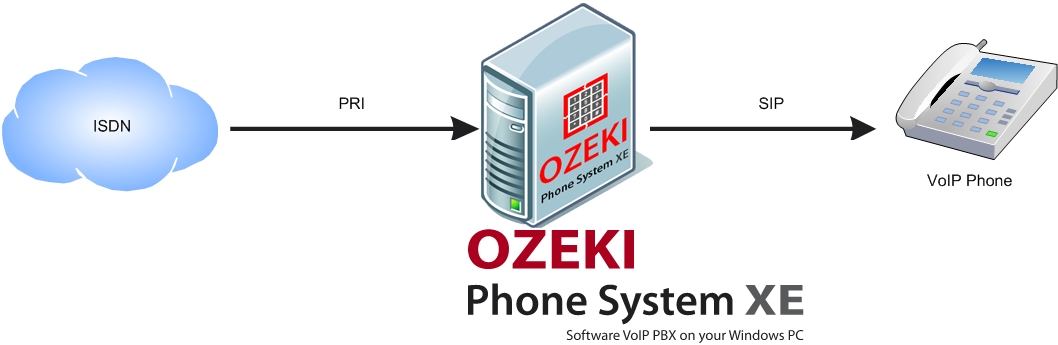
Just like Session Initiation Protocol (SIP, a protocol, which defines how to begin, maintain and end a multimedia sessionover the Internet) provides connection between a server and an IP (Internet Protocol, which defines data transmission over the Internet) end, it connects the ISDN Network to a server, in our case to the server of the Ozeki Phone System. As Figure 1 shows, that server can be connected to any VoIP phone within the local network.
PRI provides telecommunication services to offices, based on the T-carrier (T1) line in the US and Canada, and the E-carrier (E1) line in the rest of the world. The circuit is made of two pairs of copper lines between a modem from a service provider and the customer. Multiplexing/de-multiplexing techniques are used to have several channels in a single circuit.
PRI is designed for larger organisations. It has 23 B-channels (30 in Europe) and one D-Channel, while BRI (Basic-Rate Interface), its variant for individuals and small businesses, contains just two B-channels and one D-channel.
So, with PRI, you can have up to 1.544 Mbps service in the United States, Canada and Japan, or 2048 Mbps in other countries. It is typically used to connect a Private Branch eXchange (PBX, which switches inside or outside telephone calls to the appropriate extension in a local network) and a central office of the telephone company or a long distance telephone company.
Data transmission is possible at 64 Kbps on each channel. It can connect to both analog and also IP PBX systems with the possibility of a need to have a PRI Card to have the PRI circuit terminated on the PBX. It can also connect two PBX systems so it can provide as many as 30 channels between them.
Advantages of PRI if it replaces 30 separate analog lines:
- Calls would be distributed unevenly, as some analog lines would be used a lot more frequently than some other ones.
- Calls arrive directly to the desired extension without waiting for an Auto-Attendant.
- All extensions have their own number, or unique caller ID.
- Both voice and data can be transferred via the same line.
- With PRI, you can use video conferencing, faxing, send data and voice simultaneously too (on different channels).
- As the lines are digital, the voice quality is a lot higher and they are more reliable than analog lines.
- It is harder to listen to conversations on digital lines, so it gives you more privacy as well.
- You can establish calls faster with PRI.
The Ozeki Phone System serves as a server between PRI and SIP, since PRI connects it to the ISDN network, and SIP connects it to the clients. This way you do not have to worry about the type of internet connection you have, because the Ozeki Phone System will be able to provide you full service regardless of your connection.
These articles have more information about certain topics. Read them to know more:
For a better understanding, please watch our video:
What is PRI? (Video tutorial)
